Within the field of blockchain technology, Ethereum is an innovative platform that revolutionized how we conduct digital transactions and decentralized computation. Launched in 2015, Ethereum is now the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap, but its value isn’t just financial—it’s the backbone of an entire ecosystem of decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, NFTs, and more.
So, what makes Ethereum so special? Let’s dive in.
Understanding Ethereum: The basics

Unlike Bitcoin, which was primarily created as digital money, Ethereum was conceived with a broader vision. Ethereum’s secret sauce is its ability to execute smart contracts—self-running programs that do exactly what they’re programmed to do, with no middlemen.
Imagine a vending machine: you put in money, press a button, and the machine gives you your snack. No cashier, no human error, just automatic execution. That’s how smart contracts work on Ethereum, but instead of dispensing candy bars, they handle everything from lending money to managing digital art ownership.
Ethereum’s network is powered by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which processes these smart contracts across thousands of computers (nodes) worldwide. Since no single entity controls the network, Ethereum is highly secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship.
But how does Ethereum stay secure and keep things running smoothly? It uses a system called proof-of-stake (PoS), where validators (instead of miners) confirm transactions. These validators stake their own ETH as collateral to keep them honest. If they try to cheat the system, they lose their stake, so they have every incentive to play fair.
Deep understanding of the Ethereum ecosystem
Blockchain technology
At its core, Ethereum utilizes blockchain technology—a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers securely and transparently. However, Ethereum takes this technology a step further. While Bitcoin’s blockchain-primarily records financial transactions, Ethereum’s blockchain can store and execute computer code, known as smart contracts.
Each block in the Ethereum blockchain contains not just transaction records but also the most recent state of all smart contracts. This enables applications in various fields, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to supply chain management, ensuring that these applications run exactly as programmed without any possibility of downtime, censorship, or fraud.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts are perhaps Ethereum’s most revolutionary feature. These self-executing contracts have their terms directly written into code. Think of them as digital vending machines: just as a vending machine automatically dispenses a soda when you insert the correct amount of money, smart contracts automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met.
What makes these contracts special is their ability to run without any intermediary. They can facilitate complex transactions, manage digital assets, and even run entire organizations without human intervention. Even more remarkably, once deployed, smart contracts can’t be shut down or altered, even by their creators, ensuring true decentralization.
Decentralized applications (dApps)
Developers can create decentralized applications, or dApps, by building on smart contracts. Unlike traditional applications that run on centralized servers, dApps operate on Ethereum’s decentralized network. This means they can’t be shut down by governments or other authorities, making them censorship-resistant.
The Ethereum ecosystem hosts thousands of dApps across various categories:
- Financial services (lending, borrowing, trading)
- Gaming and entertainment
- Social media platforms
- Supply chain management solutions
- Digital identity systems
Ethereum’s evolution: Key upgrades
Ethereum has undergone several upgrades since its inception, each improving its scalability, security, and efficiency.
Frontier (2015): Ethereum’s launch
The Frontier release marked Ethereum’s official launch, allowing developers to create and deploy smart contracts. Miners could validate transactions using the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, similar to Bitcoin. This foundational phase established Ethereum’s network and set the stage for rapid adoption.
The DAO Fork (2016): A defining moment
In 2016, Ethereum faced a critical challenge when The DAO, a decentralized autonomous organization, suffered a security breach, losing over 3.6 million ETH. To rectify this, the Ethereum community executed a hard fork, creating two blockchains: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC). This event demonstrated Ethereum’s adaptability and community-driven governance.
The Merge (2022): Transition to proof of stake
One of Ethereum’s most significant milestones was “The Merge,” which transitioned the network from PoW to proof-of-stake (PoS). This shift reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by 99.9%, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly. The PoS model allows users to stake ETH to validate transactions and secure the network instead of using energy-intensive mining.
Dencun upgrade (2024): Scaling the network
In March 2024, Ethereum introduced the Dencun upgrade, implementing proto-danksharding (EIP-4844). This innovation reduced transaction fees on layer-2 solutions, improved data availability, and enhanced network scalability. By making transactions more affordable, Dencun encouraged broader adoption and increased efficiency.
Pectra upgrade (2025): Latest enhancements
As of early 2025, the network is preparing for the Pectra upgrade, which aims to improve wallet functionalities and validator operations. Currently undergoing testing on the Holesky and Sepolia testnets, the mainnet launch is anticipated in April 2025. These enhancements focus on user experience and further scalability improvements.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin: Understanding the differences

People often compare Ethereum to Bitcoin, but they serve different purposes. Think of Bitcoin as digital gold—a store of value that’s slow and steady. Ethereum, on the other hand, is digital oil—fuel for a programmable blockchain.
| Feature | Ethereum | Bitcoin |
| Purpose | Programmable platform | Digital currency |
| Consensus | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Proof of Work (PoW) |
| Speed | Faster transactions | Slower transactions |
| Supply | No fixed limit | Slower transactions |
Understanding ETH
ETH, or Ether, serves as the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. While it can be used like Bitcoin for sending, receiving, or storing value, ETH plays a crucial role in network operations:
- It serves as “gas” to execute smart contracts
- Users pay fees in ETH for network transactions
- It’s often described as “digital oil” compared to Bitcoin’s “digital gold.”
ETH price history
ETH has experienced significant price fluctuations influenced by technological advancements, market dynamics, and regulatory developments.
2015-2016: Inception and early growth
ETH’s journey began with its price starting at approximately $0.42. By the end of that year, it had risen to around $0.90, reflecting growing interest in its blockchain capabilities beyond cryptocurrency. In March 2016, ETH’s price crossed the $10 mark, reaching $10.03, signaling increased adoption and investor confidence.
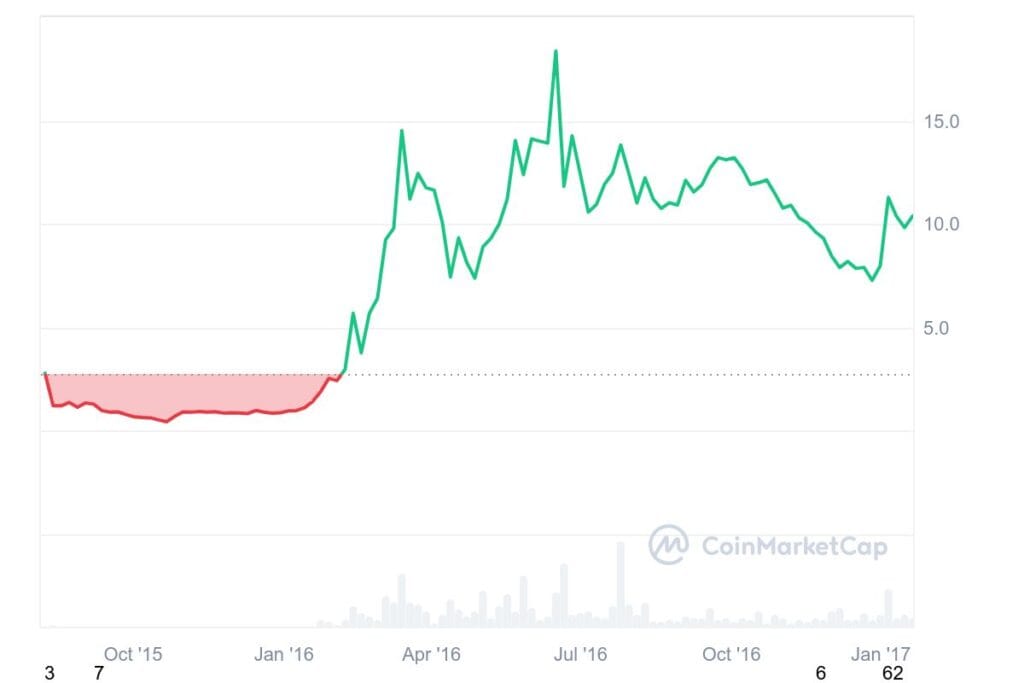
2017: Mainstream recognition and volatility
The year 2017 marked Ethereum’s entry into mainstream consciousness. Starting below $10, it surged to over $300 by mid-year. However, this rapid ascent was followed by a decline below $200, highlighting the market’s volatility. Renewed investor enthusiasm propelled ETH to approximately $774.69 by year-end.
2018: Peak and subsequent decline
In early 2018, ETH’s price exceeded $1,000, reaching an all-time high of around $1,400 in January. This peak was short-lived, as the broader cryptocurrency market faced a downturn. By the end of 2018, ETH’s value had decreased to under $100, underscoring the market’s inherent volatility.
2019-2020: Recovery and technological advancements
ETH began 2019 at approximately $160, experiencing fluctuations throughout the year and closing at nearly $145. The launch of Ethereum 2.0’s phase zero in December 2020, introducing staking mechanisms, played a pivotal role in its resurgence. By the end of 2020, ETH’s price had risen to over $700, reflecting a significant increase from the year’s start.
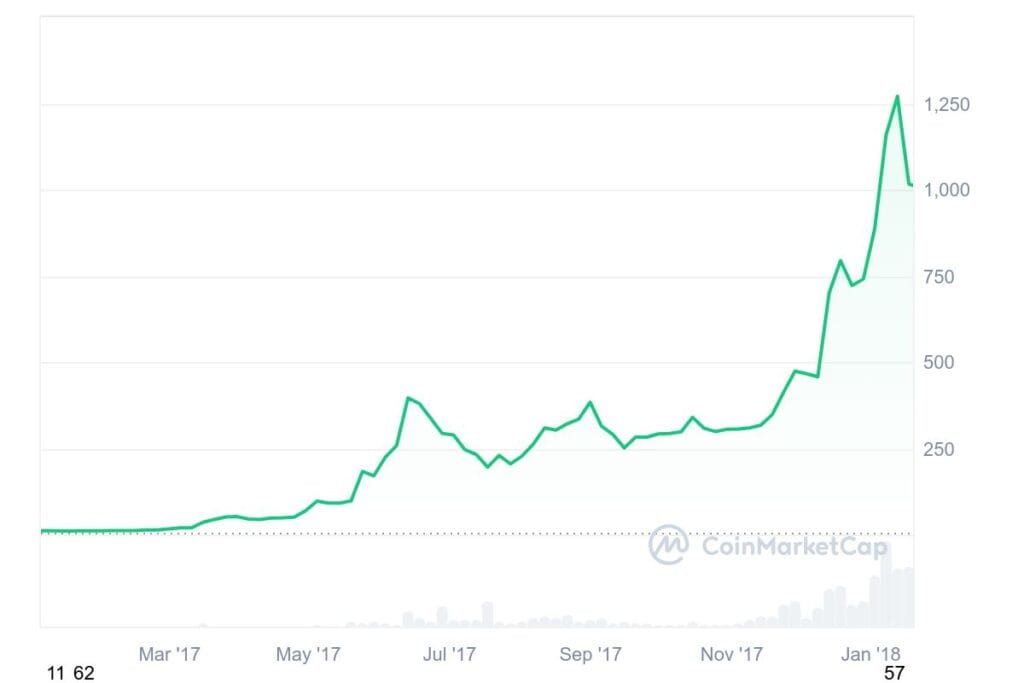
2021: New heights and market dynamics
The momentum continued into 2021, with ETH breaking previous records. In February, it neared the $2,000 mark, and by November 2021, it achieved an all-time high of approximately $4,891. This surge was driven by the increased popularity of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). However, market corrections followed, and ETH settled at around $3,700 by year-end.
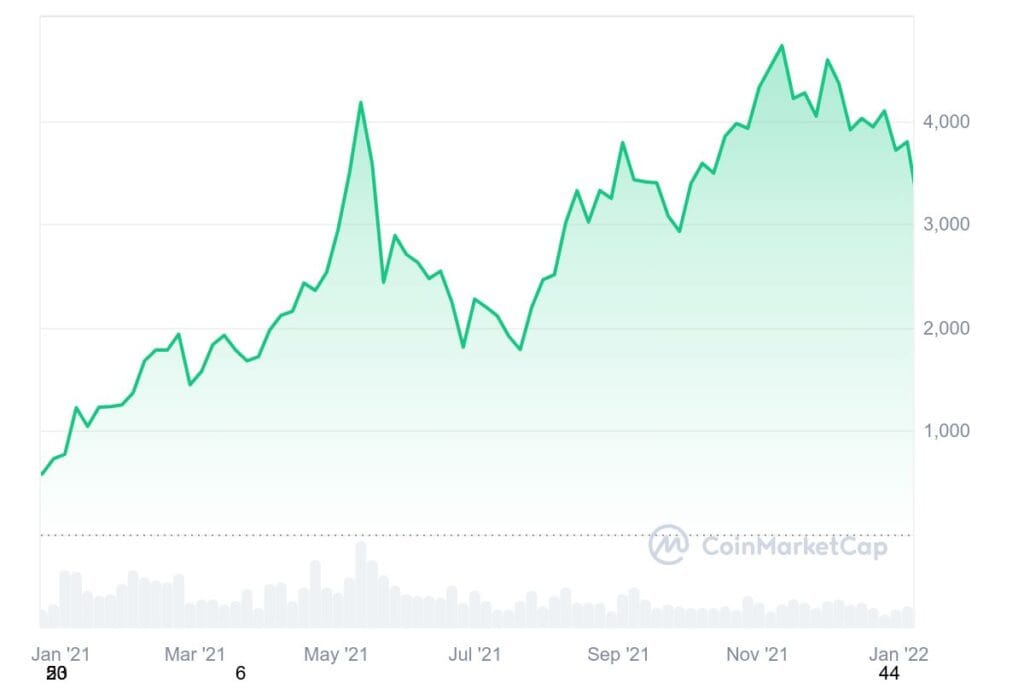
2022: Market correction and The Merge’
Entering 2022 at over $3,700, ETH faced challenges, including macroeconomic factors and industry-specific events. A significant milestone was “The Merge,” transitioning the network from a proof-of-work to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, aiming to enhance energy efficiency and scalability. Despite these advancements, Ethereum’s price declined over the year, closing at approximately $1,196.
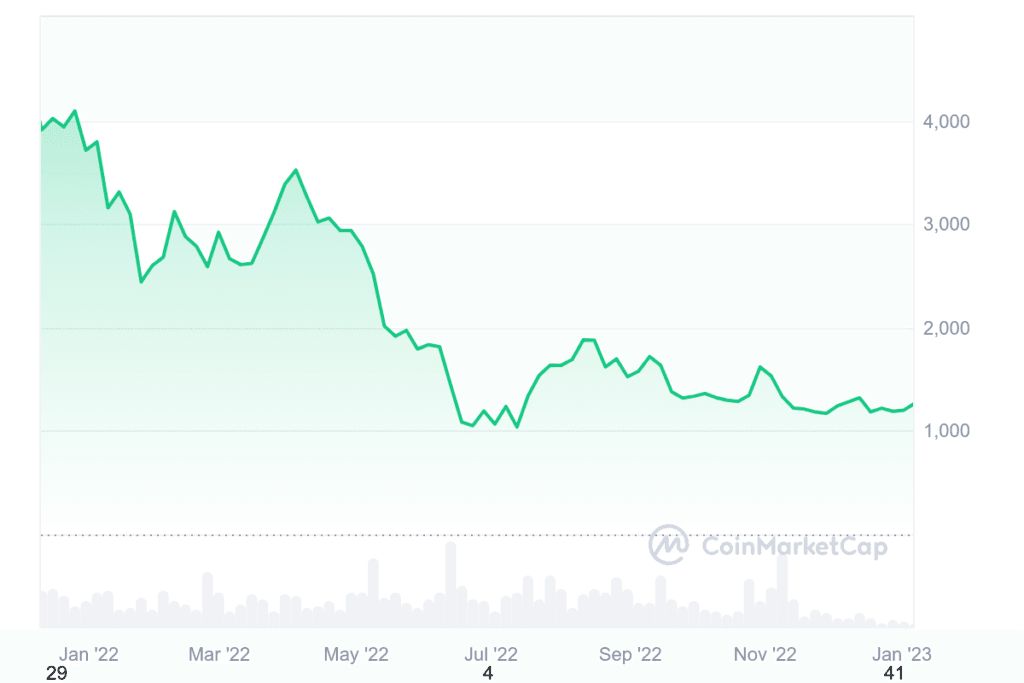
2023-2024: Recovery and competitive landscape
In 2023, ETH experienced a recovery influenced by macroeconomic factors and technological developments. By October, it was trading near $2,300, reflecting a significant yearly increase. However, by January 2025, ETH faced challenges, lagging behind competitors like Bitcoin and Solana in value and adoption. The emergence of scalable networks offering lower transaction costs contributed to this trend. As of early February 2025, Ethereum’s price is approximately $2,862.70.
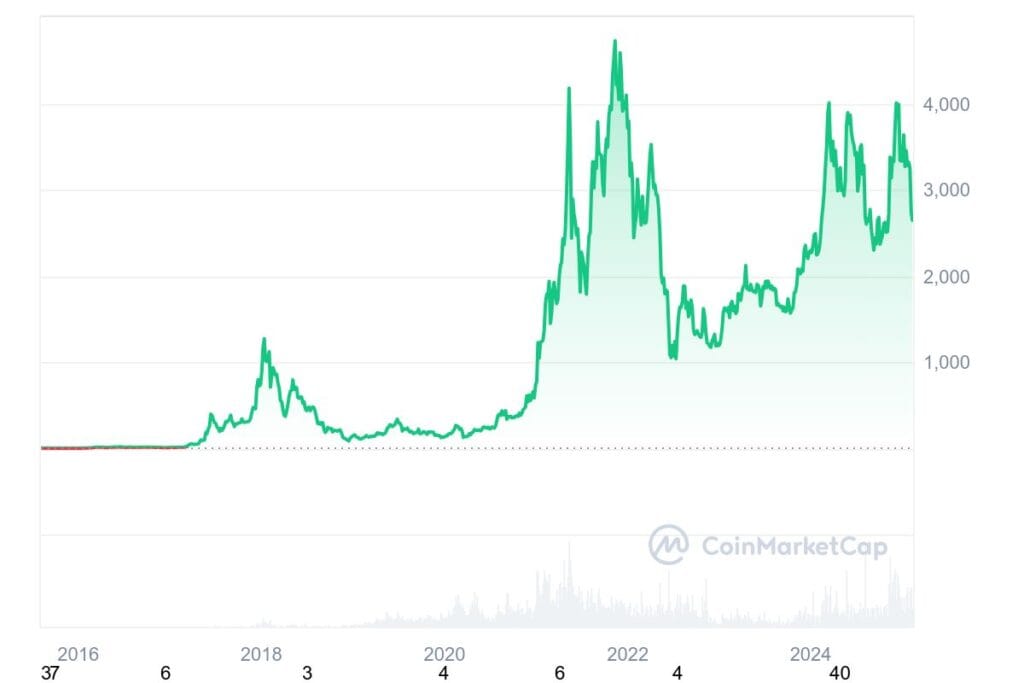
Throughout its history, ETH has demonstrated resilience and adaptability, navigating technological shifts and market dynamics. Its journey underscores the evolving nature of the cryptocurrency landscape and the factors influencing its valuation.
Types of Ethereum accounts
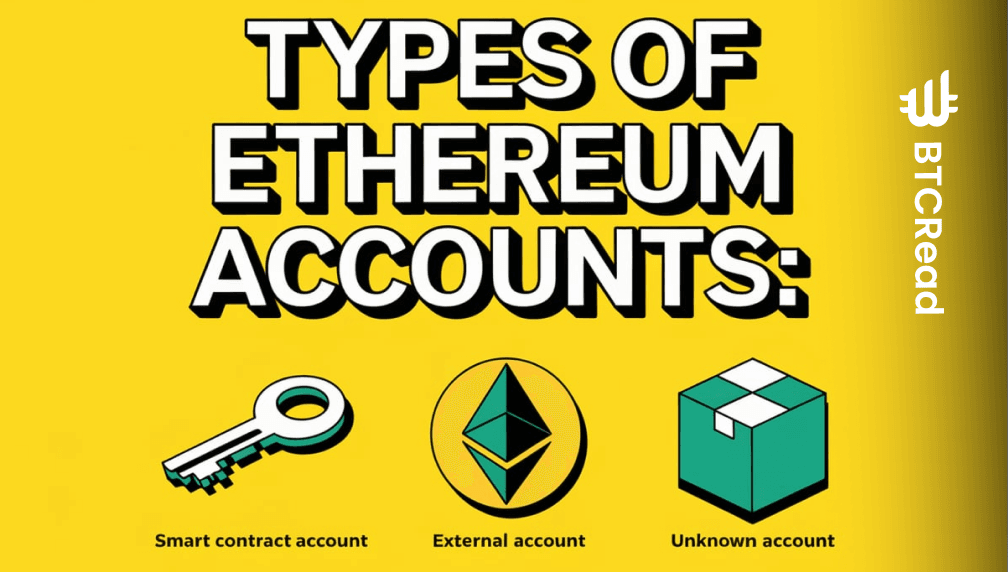
Ethereum supports two types of accounts, each serving different purposes:
1. Externally owned accounts (EOA):
- Controlled by private keys
- Can initiate transactions
- Used by individual users
- Has a public-private key pair for security
2. Contract accounts:
- Controlled by smart contract code
- Activated by transactions or messages from other contracts
- Can hold ETH balance
- Executes code when receiving transactions
Benefits and limitations of Ethereum
Ethereum offers several advantages over traditional systems:
- Availability: The decentralized network ensures constant uptime
- Privacy: Users can remain anonymous while conducting transactions
- Security: The distributed nature makes the network highly resistant to attacks
- Rapid Deployment: Enterprises can quickly implement private blockchain networks
- Data Coordination: Decentralized architecture eliminates the need for central authorities
Despite its advantages, Ethereum faces some challenges:
- Programming Complexity: Solidity, Ethereum’s primary programming language, can be difficult to learn
- Price Volatility: ETH’s value can fluctuate significantly
- Transaction Speed: While faster than Bitcoin, Ethereum’s transaction rate still faces scalability challenges
Final thoughts
Ethereum has come a long way since its launch in 2015, evolving from an ambitious blockchain experiment to a global decentralized computing platform that underpins thousands of applications. With smart contracts, dApps, and continuous upgrades, Ethereum has cemented its place as a leader in blockchain technology.
One of Ethereum’s most remarkable aspects is its ability to evolve. From its proof-of-work beginnings to its current proof-of-stake model, the network has continuously adapted to overcome challenges like scalability, energy consumption, and transaction costs. The recent Pectra upgrade is yet another example of how Ethereum remains at the forefront of innovation, striving for efficiency, security, and usability.
That said, Ethereum is not without its hurdles. Competition from other blockchains like Solana and Avalanche, along with ongoing concerns about gas fees and network congestion, means Ethereum must continue improving to maintain its dominance. But if history has shown us anything, it’s that Ethereum has a resilient community of developers, users, and businesses willing to push the technology forward.
FAQs
Ethereum is a decentralized computing platform that enables smart contracts and dApps, while Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency designed for peer-to-peer transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain that automatically enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met.
Ether (ETH) is Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, used to pay for transaction fees (“gas”) and secure the network through staking.
Ethereum relies on a decentralized network of nodes and cryptographic security to ensure transactions and smart contracts remain tamper-proof.
Ethereum 2.0 refers to Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which reduced energy consumption by 99.9% and improved scalability.
dApps (decentralized applications) run on Ethereum’s blockchain, offering censorship-resistant services in finance, gaming, social media, and more.
Gas is the fee required to process transactions and smart contract executions, paid in ETH and determined by network demand.
Ethereum is the most established smart contract platform but faces competition from Solana (faster transactions) and Cardano (scientific approach to blockchain).
Ethereum is the backbone of DeFi, enabling lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming without banks or intermediaries.
Ethereum struggles with high gas fees, network congestion, and competition from newer blockchains offering faster and cheaper transactions.