Ethereum’s on-chain activity has undergone shifts in 2024, with decentralized exchanges leading transaction fees.
CoinShares’ Q4 2024 report highlights Uniswap’s dominance, showing that stablecoin movements and DEX usage now exceed standard ETH transfers.

This shift reinforces Ethereum’s evolving role as a financial settlement layer rather than just a payment network. Layer 2-related fees, once high, have dropped due to the impact of EIP-4844, which introduced cost-saving measures.
Despite transaction fee expenditures in 2023 and 2024 being similar in dollar terms, Ethereum’s supply burn has declined. Two factors explain this: gas prices were higher in 2023, and ETH’s market price remained elevated in 2024.
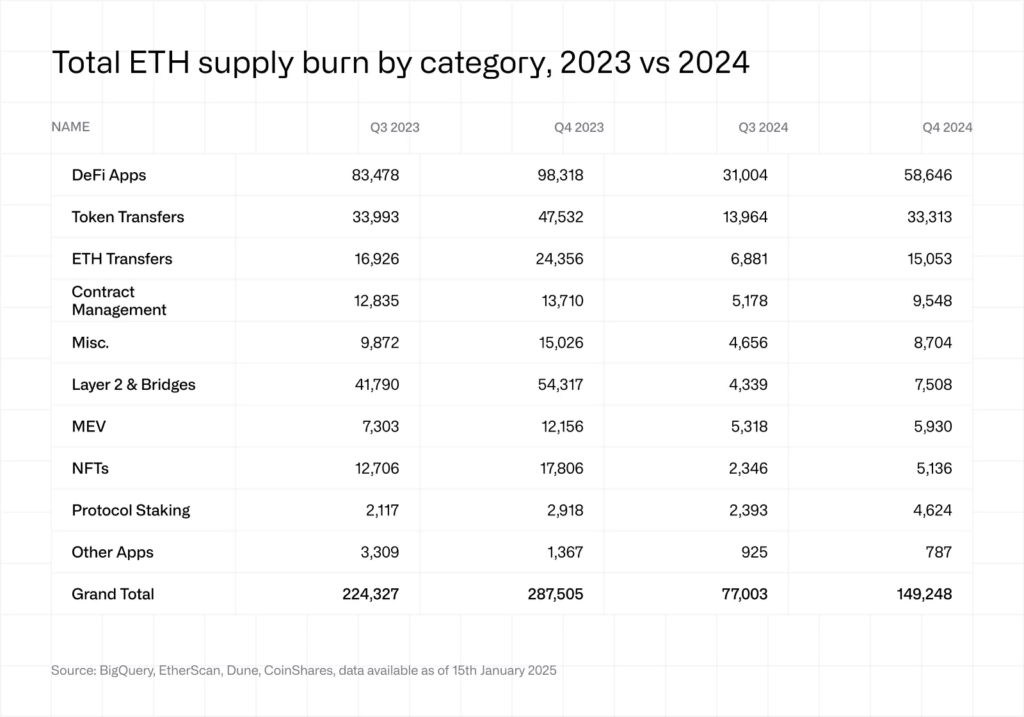
With ETH valued higher in USD, less ETH needed to be burned to maintain equivalent fee expenditures. This has altered supply dynamics compared to previous years.
Ethereum L2 fees drop with EIP-4844
A key trend in 2024 is the weakening link between Ethereum’s gas prices and ETH’s market cycles. Historically, rising ETH prices aligned with increased network usage and higher gas fees.
This pattern suggested a strong relationship between speculation-driven activity and gas demand. However, in 2024, gas prices have not reached previous peaks, suggesting a potential shift in user behavior.
Decoupling of gas costs from ETH pricing can be an indicator of wider blockchain usage trends. Greater numbers of transactions are shifting away from Ethereum Layer 1 and toward Layer 2 solutions and other networks.
While users choose lower-cost options, Ethereum gas pricing can decouple from ETH speculative cycles. In the long term, this can result in a healthier network in which gas prices and market pricing adapt in relation to real-world usage rather than speculative cycles.